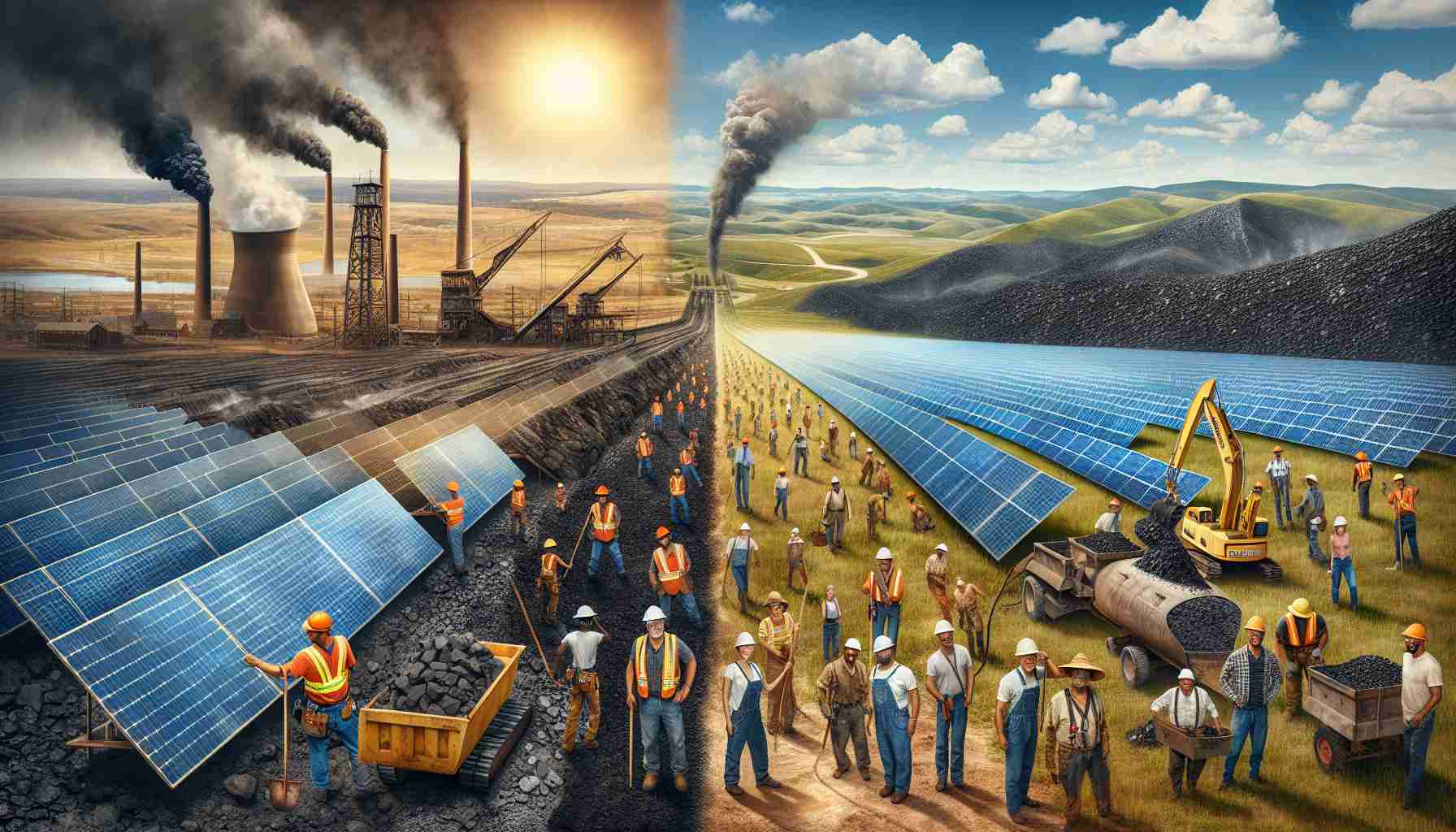
In a significant transformation for South Texas, a coal plant is set to be decommissioned and replaced with a solar and battery facility. This bold transition, supported by a hefty $1.4 billion grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, aims to promote clean energy and protect rural employment.
San Miguel Electric Cooperative Inc. (SMECI), located in Atascosa County, will lead this groundbreaking initiative. The cooperative has operated a coal plant since 1982, known for being one of Texas’s leading mercury polluters. Many local residents have been adversely affected by toxic groundwater contamination resulting from the plant’s coal ash ponds.
This new grant not only underscores a commitment to environmental reform but is expected to create around 600 jobs and reduce climate pollution by an impressive 1.8 million tons annually, equivalent to removing about 446,000 cars from Texas roads.
With the sun shining abundantly in South Texas, the aging coal plant will soon transition to a solar facility capable of generating 600 megawatts of power and equipped with battery storage for enhanced grid stability. This upgrade will enhance energy efficiency, ensuring smoother energy distribution and greater responsiveness to demand fluctuations.
This shift marks a pivotal step toward a cleaner energy future for Texas, moving the state further away from coal dependency while bolstering local economies and preserving jobs. As the country embraces renewable energy, this project sets a prime example of sustainable progress.
Transforming South Texas: Solar Energy Project Set to Replace Coal Plant
The Transition to Renewable Energy in South Texas
In a groundbreaking shift towards sustainability, South Texas is making headlines with the planned decommissioning of a coal plant, to be replaced by a modern solar and battery storage facility. This transformation, spearheaded by the San Miguel Electric Cooperative Inc. (SMECI) in Atascosa County, is a pivotal move in the battle against climate change and local environmental concerns.
Significant Investment and Job Creation
The project is bolstered by a substantial $1.4 billion grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, demonstrating a strong government commitment to promoting clean energy. This investment is projected to foster approximately 600 jobs, thus aiding both local economies and communities reliant on energy sector employment.
Environmental Impact and Community Health
The long-standing coal operation was infamous for its significant mercury emissions and groundwater contamination due to toxic coal ash residues. The transition to solar energy not only aims to mitigate these environmental hazards but is also anticipated to reduce climate pollution by 1.8 million tons annually. This pollution reduction is comparable to taking 446,000 cars off the roads of Texas, making a considerable impact on public health and ecological preservation.
Specifications of the New Solar Facility
The new solar facility will harness the abundant sunlight of South Texas, boasting an impressive capacity to generate 600 megawatts of power. Additionally, it will come equipped with battery storage systems designed to enhance grid stability, ensuring that energy delivery is both efficient and responsive to the demands of the local population.
Pros and Cons of the Transition
Pros:
– Environmental Restoration: Reduction in pollution levels and improvements to local ecosystems.
– Economic Growth: Job creation and investment in local economies.
– Renewable Energy Leadership: Positioning Texas as a leader in renewable energy initiatives.
Cons:
– Transition Challenges: Potential job displacement in the coal sector before new jobs are created.
– Initial Costs: High upfront investment required for solar technology and infrastructure.
Future Trends and Insights
As the U.S. transitions to greener energy, projects like this one set a precedent for other regions to follow. The SMECI initiative could serve as a model for similar transformations across the country, illustrating that modernization in energy production not only meets environmental goals but also stimulates local economies.
Additionally, as technologies advance, the effectiveness and affordability of solar energy solutions, including battery storage, are expected to improve, further driving the national agenda towards renewable energy sources.
Conclusion: A Template for Sustainable Progress
The decommissioning of the coal plant and the establishment of a solar and battery facility reflect a significant evolution in South Texas’s energy landscape. By prioritizing clean energy, the project not only addresses pressing environmental issues but also strengthens job markets and local economies. As similar projects gain momentum across the country, they mark a definitive move towards a sustainable energy future.
For more details on renewable energy initiatives, visit Energy.gov.